Plant Structures
Plant Structures
SC.912.L.14.7 Relate the structure of each of the major plant organs and tissues to physiological processes.
What You Need to Know
You need to know how the structures of plant tissues and organs are directly related to their roles in physiological processes.
- Plant organs are limited to roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruit and cones.
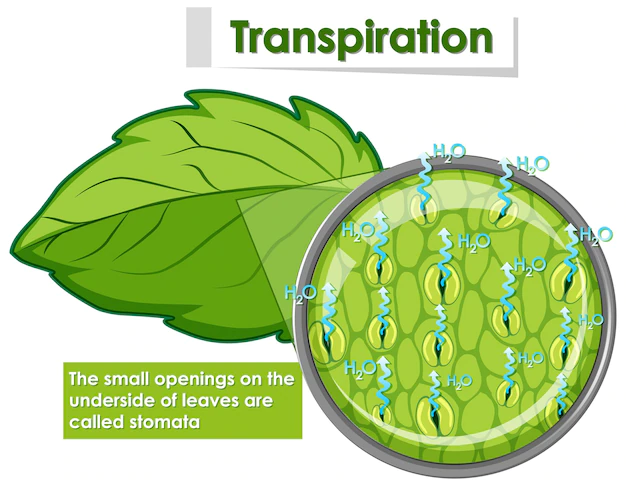
- Physiological processes are limited to photosynthesis, cellular respiration, transpiration, and reproduction.
- Plant tissues are limited to meristematic, ground, dermal and vascular tissues.
- Plant structures are limited to cambium, guard cells, phloem, seed, stomata and xylem.
Plant Organs
Physiological processes
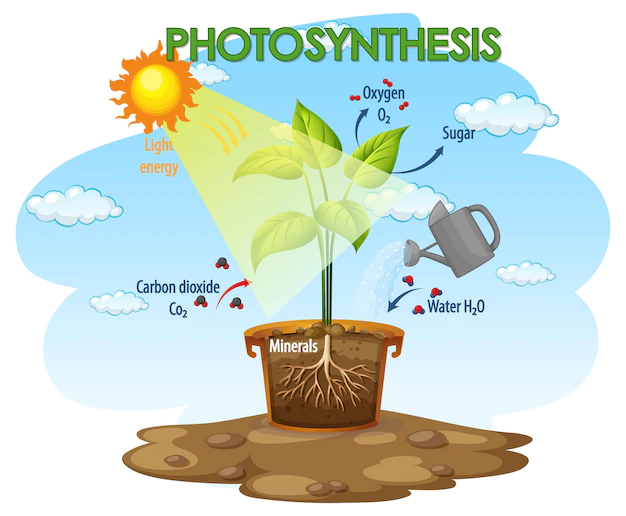
Photosynthesis is the process where plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create oxygen and energy (in sugar form).
Cellular Respiration is done in the mitochondria. The process breaks down glucose (sugar) and oxygen to release energy (ATP) and Carbon dioxide.
Plant Reproduction uses flowers or cones to spread sperm cells (from anther) to egg cells found in the stigma (female part) of the flower.
Plant Tissues
Plant Structures
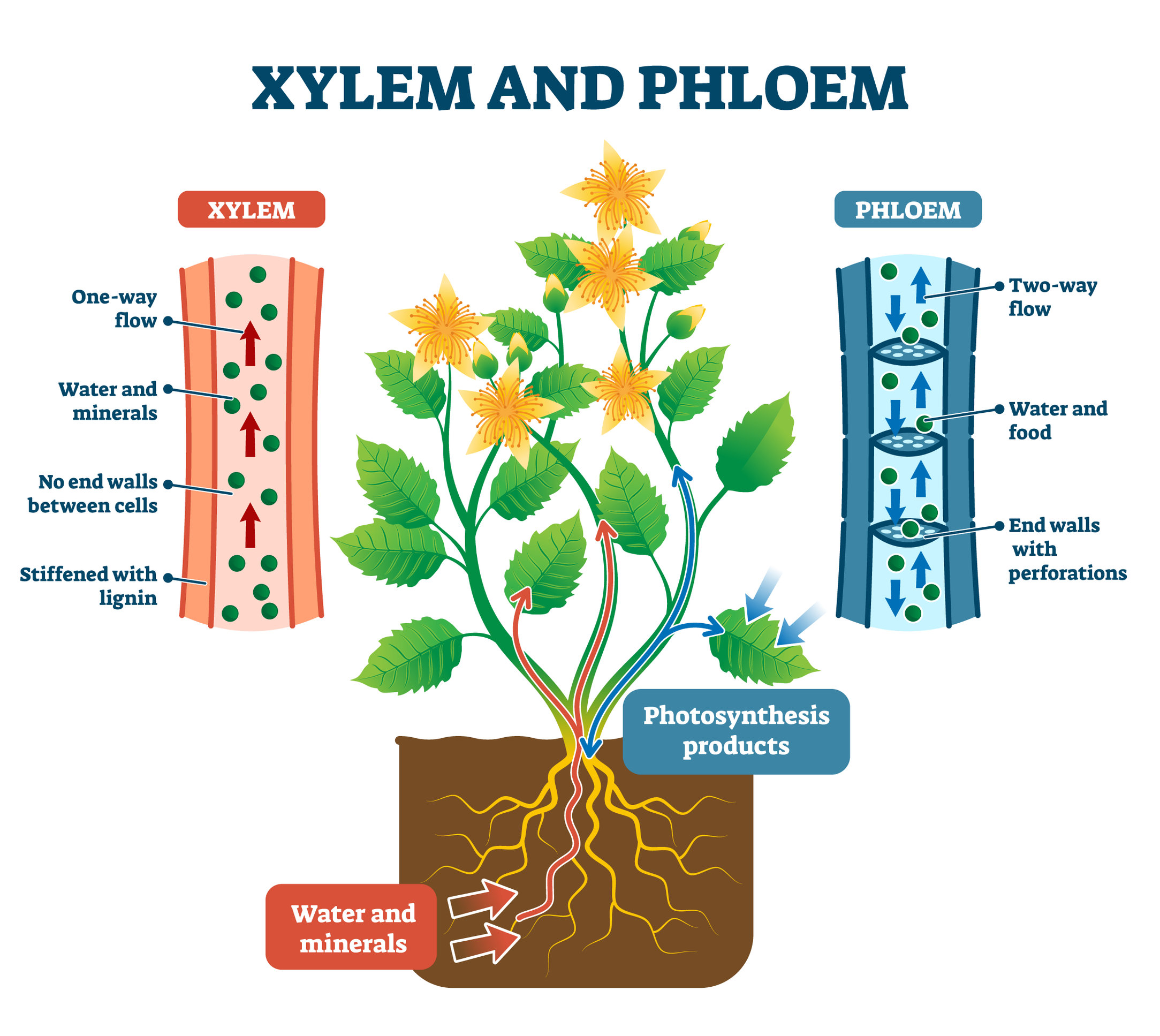
Xylem is the tissue that transports water from the soil to the leaves.
Phloem is the tissue that transports minerals and food from the soil to the leaves.