Genetics
1. What is Genetics?
Genetics is the study of how traits are inherited or passed between generations.
 2. Who is Gregor Mendel?
2. Who is Gregor Mendel?

The father of Genetics! He experimented with sweet pea plants in the 1800s.
With this experiment, he made 3 laws and called them: The Laws of Heredity
3. What's an allele?
Alleles are the different forms of the same gene(trait)
So, the TRAIT is having hair while the ALLELE is blonde color or brunette colored hair.
Dominant Alleles: The controlling allele, Usually shown with a capital letter (B)
Recessive Alleles: The hidden allele, Usually shown with a lowercase letter (b)
4. Law of Dominance
The Dominant allele will prevent the recessive allele from being expressed.
The Recessive allele will appear when it's paired with another recessive allele in the offspring.
Allele pairs must separate so that each gamete created during meiosis has only ONE allele from each pair allele coding for the same trait.
6. Law of Independent Assortment

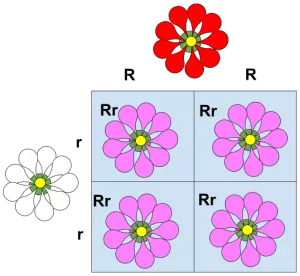
7. Punnett Squares: Monohybrid
a cross between two heterozygous individuals.
RATIO: 1: 2:1 Genotype & 3:1 phenotype ratio in the offspring.
Probability: 75% or 3/4 dominant phenotype
8. Punnett Squares: Dihybrid
A Dihybrid Cross contains 16 Boxes; reveals two traits for both parents.
A cross with two heterozygous individuals would reveal a RATIO of 9:3:3:1 phenotype in offspring
9. Patterns of Inheritance
Sex-Linked Traits
Traits (genes) located on the X chromosome can have effects on the offspring. They can have the trait, carry the trait in their genes, or not have the trait at all.
Multiple Alleles
People also have this too!
Polygenic Inheritance
150 genes have now been identified as having a direct or indirect effect on skin color.
Incomplete Dominance
Neither allele is dominant! So it displayed as a mix
Here is a Homozygous Red flower with a
Homozygous White Flower to create a
Heterozygous Pink Flower
The record of descent of an organism. Helps determine inheritance in families and in animals!